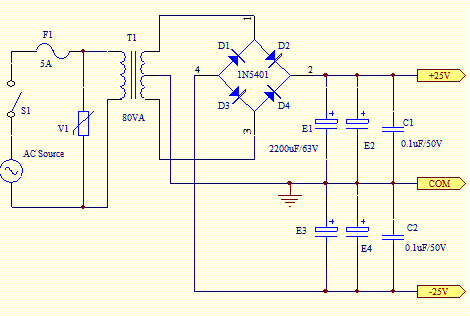
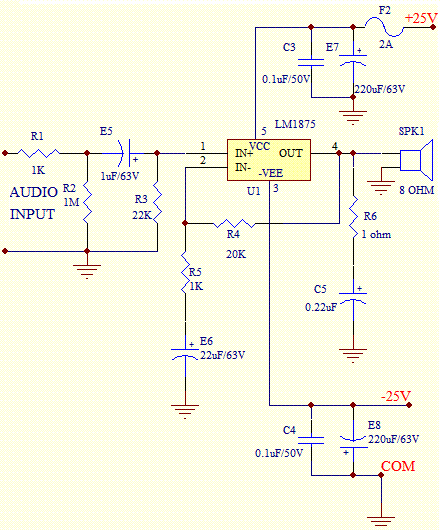
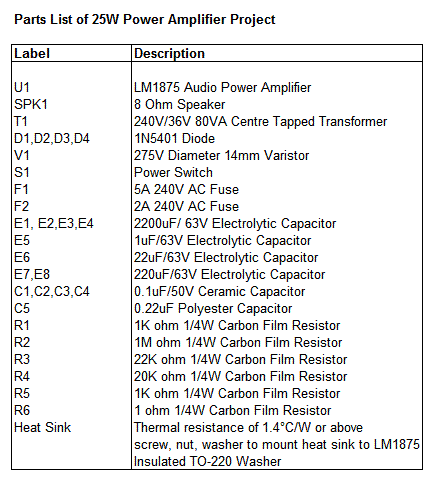
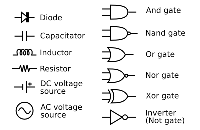
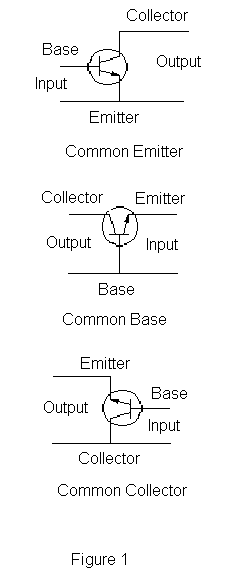
A
circuit diagram (also known as an electrical diagram, elementary diagram, or electronic
schematic) is a simplified conventional pictorial representation of an
electrical circuit. It shows the different components of the circuit as simplified standard symbols, and the
power and
signal connections between the devices. Arrangement of the components interconnections on the diagram does not correspond to their physical locations in the finished device.
Unlike a
block diagram or layout diagram, a circuit diagram shows the actual wire
interconnects being used. The diagram does not show the arrangement of components. A drawing meant to depict what the circuit actually looks like is called "artwork" or "
layout".
Circuit diagrams are used for the design (
circuit design), construction (such as
PCB layout), and maintenance of electrical and electronic equipment.
Legends
On a circuit diagram, the symbols for components are labelled with a descriptor (or reference designation) matching that on the list of parts. For example, C1 is the first
capacitor, L1 is the first
inductor, Q1 is the first
transistor, and R1 is the first
resistor (note that it isn't written R
1, L
1,…). The letters that precede the numbers were chosen in the early days of the electrical industry, even before the
vacuum tube (thermionic valve), so "Q" was the only one available for semiconductor devices in the mid-twentieth century . Often the value or type designation of the component is given on the diagram beside the part, but detailed specifications would go on the parts list.
Symbols
Circuit diagram symbols have differed from country to country and have changed over time, but are now to a large extent internationally standardized. Simple components often had symbols intended to represent some feature of the physical construction of the device. For example, the symbol for a resistor shown here dates back to the days when that component was made from a long piece of wire wrapped in such a manner as to not produce inductance, which would have made it a
coil. These wirewound resistors are now used only in high-power applications, smaller resistors being cast from
carbon composition (a mixture of
carbon and
filler) or fabricated as an insulating tube or chip coated with a metal film. To illustrate this, European circuit diagrams have replaced the zig-zag symbol by a simple oblong, sometimes with the value in
ohms written inside. A less common symbol is simply a series of peaks on one side of the line representing the conductor, rather than back-and-forth as shown here.
Circuit symbols are standardized, using either
ANSI standard Y32 or
IEC standard 60617DB (a standard in database format). Different symbols may be used depending on the discipline using the drawing; for example, lighting and power symbols used as part of architectural drawings may be different from symbols for devices used in electronics.
Linkages
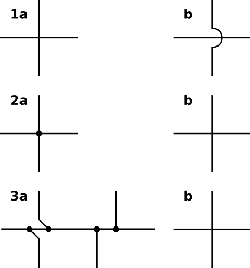

Schematic wire junctions:
1. Old style: (a) connection, (b) no connection.
2. Early CAD style: (a) connection, (b) no connection.
3. New style: (a) connection, (b) no connection.
The linkages between leads were once simple crossings of lines; one wire insulated from and "jumping over" another was indicated by it making a little semicircle over the other line. With the arrival of computerized drafting, a connection of two intersecting wires was shown by a crossing with a dot or "blob", and a crossover of insulated wires by a simple crossing without a dot. However, there was a danger of confusing these two representations if the dot was drawn too small or omitted. Modern practice is to avoid using the "crossover with dot" symbol, and to draw the wires meeting at two points instead of one. It is also common to use a hybrid style, showing connections as a cross with a dot while insulated crossings use the semicircle.
European and Australian codes
The following codes which vary slightly from the American codes are in common use in European & Australian standard electrical circuit diagrams. These codes are used for the "reference
designators" printed on PCBs (which match the corresponding ones written on the corresponding schematic).
A - Assemblies
B - Transducers (Photo cells, Inductive Proximity, Thermocouple, Flame Detection)
C - Capacitors
D - Storage Devices
E - Miscellaneous
F - Fuses
G - Generator, Battery Pack
H - Indicators, Lamps (not for illumination), Signalling Devices
K - Relays, Contactors
L - Inductors and Filters
M - Motors
N - Analogue Devices
P - Measuring/Test Equipment
Q - Circuit Breakers, Isolators, Re-closers
R - Resistors, Brake Resistors
S - Switches, Push Buttons, Emergency stops and Limit Switches
T - Transformers
U - Power Converters, Variable Speed Drives, Soft Starters, DC Power Supplies
V - Semiconductors
W - Wires, Conductors, Power, Neutral & Earthing Busses
X - Terminal Strips, terminations, joins
Y - Solenoids, Electrical actuators
Z - Filters